HYDRO 100 454GR – PN
26.50€
HYDRO 100 454GR – PN
What Is HYDRO 100?
HYDRO 100 is an elite hydrolyzed whey protein supplement, featuring bioavailable whey protein hydrolysate and whey protein isolate – two of the fastest-acting forms of whey protein available. HYDRO 100 is simple to digest and very low in lactose and fat, making it ideal for post-workout and any time of the day you want a quick and effective source of high-quality whey protein.
Why Is Whey Protein so Beneficial for Building Muscle and Burning Fat?
Proteins are a form of macronutrient composed of amino acids – the building blocks of skeletal muscle tissue. Whey protein is one of nature’s few complete sources of protein (meaning it contains all nine essential amino acids that your body needs to get through food/supplements).
Make no mistake that if you’re goal is to be healthy and fit, protein plays a pivotal role in your diet. The myriad functions protein has in the human body include neurotransmission, energy production, cardiovascular function, immune system regulation; protein is also the key regulator/substrate for building and repairing tissues (such as muscle).1
Whey refers to the milk serum byproduct produced during the curdling of milk. Whey proteins comprise roughly 1/5th of the total protein content in dairy milk, with the rest being casein proteins which digest much slower.2
Pure Nutrition offers Pure Casein Protein Powder if you want a premium-quality, slow-digesting protein supplement. (We recommend using Pure Casein prior to bedtime to protect your muscle tissue while you sleep and help you recover.)
Types of Whey Protein found in HYDRO 100
HYDRO 100 features the two fastest-absorbing forms of whey protein on the market: Whey protein hydrolysate and whey protein isolate. These forms of whey protein are extremely high in muscle-building branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) and have very low sugar and fat content. In fact, each serving of HYDRO 100 provides five grams of BCAAs and has less than one gram of sugar and less than 1.5 grams of fat.
Benefits of HYDRO 100
Since amino acids are the building blocks of proteins, whey protein hydrolysate and whey protein isolate in HYDRO 100 are the ideal forms of complete proteins to help your body repair and build lean muscle tissue (muscle is where you body stores the vast majority of amino acids).
Moreover, HYDRO 100 contains a large proportion of branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), especially L-leucine, a key BCAA that has been found to be the “launch signal” for muscle protein synthesis (MPS).3 Other evidence-based benefits of HYDRO 100 include: 4,5
- Increased anabolic effects of resistance exercise
- Support for lean body mass
- Rapidly absorbed and easy to digest
- Simple/convenient to add to one’s diet and use in recipes
- Reduce muscle tissue breakdown (catabolism)
Research is ongoing as to how much protein is optimal (especially in active individuals). In general, it is recommended to ingest at least 1 gram of protein per pound of your lean body mass. For example, if you weigh 200 lbs and are 10% body fat, you should aim for about 180 grams of protein per day (at least).
This is where HYDRO 100 can come in handy as reaching that amount through whole-food sources may be hard to accomplish for some individuals.
Pure Nutrition HYDRO 100: Why It’s the Best Hydrolyzed Whey Protein Supplement on the Market
HYDRO 100 contains both whey protein isolate and whey protein hydrolysate, which are well-tolerated by most people. You need to be wary of low-grade whey protein powders as many supplement companies these days use inferior production methods and disreputable sources for their protein, which increases the risk of certain side effects, including:
- Bloating/flatulence
- Gastrointestinal pain
- Irritable bowel
- Allergic reactions
- Nausea and headache
This is where Pure Nutrition HYDRO 100 sets itself apart from the competition, by using only premium-source whey protein and the highest quality ingredients. Not only is HYDRO 100 one of the purest whey protein powders available, it also tastes delicious and contains absolutely no gluten or tree nuts.
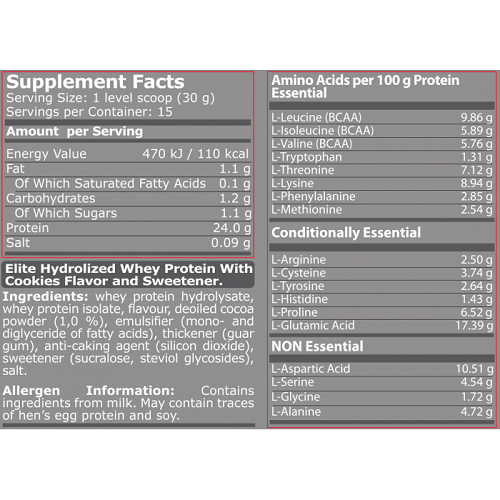
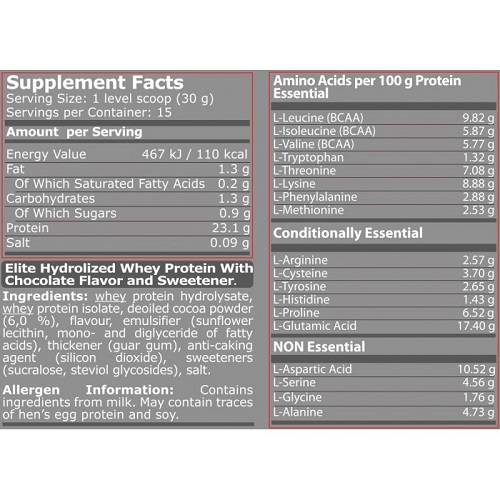
But what exactly are whey protein hydrolysate and whey protein isolate? Here’s some quick overviews:
Whey Protein Hydrolysate (WPH)
Whey protein hydrolysate (also known as hydrolyzed whey protein) is produced by enzymatically hydrolyzing (splitting the chemical bonds of) either whey protein and creating smaller amino acid chains and peptides that are essentially “pre-digested”. This makes whey protein hydrolysate rapidly absorbed and readily taken up by your skeletal muscle tissue, and it’s very easy to digest.
Whey Protein Isolate (WPI)
Whey protein isolate is over 90% protein content, typically made through ultrafiltration and an ion-exchange process that selectively filters out molecules according their ionic charge as opposed to their structural size. The result is a whey protein that is very low in lactose, fat, and carbohydrates.
Which Type of Whey Protein is Best
There is no “best” whey protein as choosing the right whey protein for ultimately comes down to your goals and other factors, such as lactose tolerability, rate of digestion, flavor, and others.
This is why Pure Nutrition offers several whey protein supplements, including Pure Whey, Whey Isolate, and more.
HYDRO 100 is ideal if you if you want an extremely low-fat, low-carb, gluten-free and easily digested protein supplement with hydrolyzed whey peptides and whey protein isolate.
References:
1. Wagenmakers, A. J. (1997). Muscle amino acid metabolism at rest and during exercise: role in human physiology and metabolism. Exercise and sport sciences reviews, 26, 287-314.
2. Basch, J. J., Douglas, F. W., Procino, L. G., Holsinger, V. H., & Farrell, H. M. (1985). Quantitation of caseins and whey proteins of processed milks and whey protein concentrates, application of gel electrophoresis, and comparison with Harland-Ashworth procedure. Journal of Dairy Science,68(1), 23-31.
3. Li, F., Yin, Y., Tan, B., Kong, X., & Wu, G. (2011). Leucine nutrition in animals and humans: mTOR signaling and beyond. Amino Acids, 41(5), 1185-1193.
4. Ha, E., & Zemel, M. B. (2003). Functional properties of whey, whey components, and essential amino acids: mechanisms underlying health benefits for active people (review). The Journal of nutritional biochemistry,14(5), 251-258.
5. Schaafsma, G. (2006). Health issues of whey proteins: 1. Protection of lean body mass. Current Topics in Nutraceutical Research, 2, 4, 113-122.
– Να μη γίνεται υπέρβαση της συνιστώμενης ημερήσιας δόσης.
– Το προϊόν αυτό δεν προορίζεται για την πρόληψη, αγωγή ή θεραπεία ανθρώπινης νόσου. Συμβουλευτείτε τον γιατρό σας αν είστε έγκυος, θηλάζετε, βρίσκεστε υπό φαρμακευτική αγωγή ή αντιμετωπίζετε προβλήματα υγείας.
– Να φυλάσσεται μακριά από τα μικρά παιδιά.
- Food supplements should not be used as a substitute for a balanced diet.
- Do not exceed the recommended daily allowance.
- This product is not intended for the prevention, treatment or cure of a human disease. Consult your doctor if you are pregnant, breast-feeding, under medication or have a health problem.
- Keep out of the reach of small children.



 Ελληνικα
Ελληνικα







