PLANT PROTEIN 908 GR – PN – CHOCOLATE
33.50€
Pure Nutrition has created plant protein powder with six unique plant sources for a complete amino acid profile, high bioavailability, low allergy potential and easy digestion to give your body the nutrients it needs!
PLANT PROTEIN 454GR – PN
Being on a vegetarian or vegan diet can make meeting your protein demands through whole foods quite a challenge. Unfortunately, many protein powders on the market are made from animal products that aren’t suitable for plant-based lifestyles.
This is why Pure Nutrition created Plant Protein – a great tasting, plant-based protein powder made with six unique plant sources for a complete amino acid profile, high bioavailability, low allergy potential, and easy digestibility to give your body the nutrients it needs to recover, repair, and perform at peak capacity.
Not only does Pure Nutrition Plant Protein come packed with essential amino acids and beneficial micronutrients, but also digestive enzymes and probiotics to help fortify your digestive function and gut health. To maintain complete compilability with plant-based lifestyles, Pure Nutrition Plant Protein is naturally flavored and made with natural sweeteners, including erythritol and stevia.
Each serving of Pure Nutrition Plant Protein contains:
- 21 grams of high-quality plant protein from six different plant sources (providing over 3.5 g of BCAAs)
- Added proteolytic enzymes and beneficial probiotics for optimizing digestion and nutrient absorption
- Only 1.7 g of carbohydrates and virtually no sugar
- Less than 120 calories and 3 g of fat
- Natural chocolate flavor and natural sweeteners like stevia
- No soy, gluten, lactose, dairy, artificial flavors, aspartame, or acesulfame-K
Pure Nutrition Plant Protein comes in several size options: 1 lb (15 servings), 2 lb (30 servings), and 4 lb (60 servings), making it a fantastic value for those who want a high-quality vegan protein powder.
Benefits of Pure Nutrition Plant Protein
Pure Nutrition Plant Protein features six of the most prized plant protein sources, including pea protein isolate, rice protein concentrate, carob germ flour protein, sunflower seed protein, pumpkin seed protein, and hemp protein.
The conundrum many people on a plant-based diet face is getting enough protein and essential amino acids through whole foods alone since plants don’t have as much protein content as things like eggs, chicken, beef, cow’s milk, and fish.
Considering that research suggests active individuals need around 1 g of protein per pound of body weight, daily, the amount of whole peas, rice, sunflower seeds, etc. that you would need to eat to meet those needs is generally not practical.1
For example, 200 grams of green peas provides roughly 160 calories, 29 grams of carbohydrates (11 of which are sugars), and 10 grams of protein. That means an athlete or gym-goer who weighs 170 lbs would have to eat a whopping 3,400 grams of green peas every day just to meet their protein requirements! Even if you did eat all those peas, you’d be consuming 493 grams of carbs and 187 grams of sugar just to get 170 grams of protein. Obviously, that’s not going to be good for your health and longevity.
As such, being on a vegan or plant-based diet makes it very challenging to meet your protein needs solely through whole foods since most plant foods have a much higher carbohydrate content than they do protein.
This is where Pure Nutrition Plant Protein comes in handy by providing a complete amino acid profile (like whey protein does) from six different highly bioavailable, hypoallergenic, and easily digestible plant sources. These plant protein sources are made through cutting-edge extraction and filtration processes that remove virtually all of the sugar and starch, making them much lower in calories and very high in protein.
With little else in the way of plant-based alternatives, it’s sensible for most all vegans and vegetarians to consider using plant-based protein powder.
Benefits of Pure Nutrition Plant Protein:
- Complete amino acid profile that increases the anabolic response to vigorous exercise2
- Hypoallergenic, plant-based protein sources that support muscle tissue growth and repair3
- Helps vegans, vegetarians, and health-conscious individuals meet their daily protein requirements
- Support healthy cholesterol and blood pressure4
- Easy to digest and promotes an alkaline diet5
- Contains digestive enzymes, probiotics, and other crucial micronutrients
- Comes in delicious chocolate flavor and mixes easily for on-the-go use
Whether you’re an athlete looking to build and repair muscle or a health-enthusiast searching for a high-quality, vegan-friendly protein powder to help you meet your daily protein needs, Pure Nutrition Plant Protein is the ideal choice.
What Makes Pure Nutrition Plant Protein the Best Plant-Based Protein Powder?
Pure Nutrition Plant Protein is gluten-free, soy-free, lactose-free, dairy-free, aspartame-free, and suitable for those on plant-based diets. We use six different plant protein sources, creating one of the most hypoallergenic and easy-to-digest plant protein powders available. Pure Nutrition Plant Protein has a well-balanced amino acid profile—high in branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) —which support lean body mass. Studies also suggest that the plant proteins in Pure Nutrition Plant Protein may play a role in reducing the risk of cancer, enhancing cardiovascular function, and inhibiting inflammation.6, 7
Moreover, our blend of natural flavors and natural sweeteners yields a plant-based protein powder blend that you will actually look forward to consuming. Many people will even use Pure Nutrition Plant Protein for making delicious, healthy vegan recipes.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: I’m lactose intolerant, can I still use Pure Nutrition Plant Protein?
A: Certainly, Pure Nutrition Plant Protein is lactose-free.
Q: I’m allergic to dairy milk, is Pure Nutrition Plant Protein safe for me?
A: Pure Nutrition Plant Protein does not contain dairy ingredients and is a safe alternative to milk/dairy protein sources.
Q: Can I combine Pure Nutrition Plant Protein with my other powdered supplements like creatine, glutamine, etc?
A: Yes, that’s absolutely fine.
Q: Does it matter what liquid I mix Pure Nutrition Plant Protein in?
A: No, Pure Nutrition Plant Protein mixes easily in most any liquid (note that it tends to mix best in liquids that are at room temperature).
Q: Can I use Pure Nutrition Plant Protein in cooking/baking recipes?
A: Absolutely; due to its taste and physical properties, Pure Nutrition Plant Protein may be used as a replacement or additive in a variety of food recipes to increase protein content and enhance flavor.
Dissolve in 250 ml water or vegetable milk and take:
- Before and after training
- As a substitute for nutrition when needed
- Between main meals

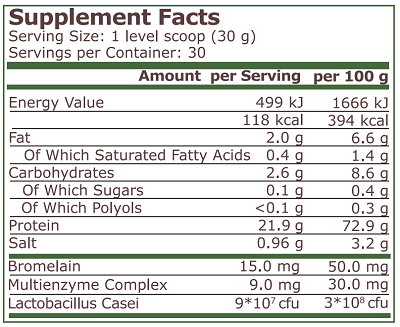
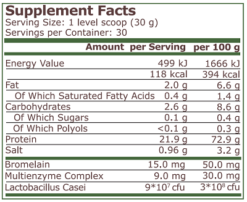
| SUPPLEMENT FACTS | |
| Serving Size | 1 level scoop (30 g) |
| Servings | 60 |
| AMOUNT PER SERVING | |
| Energy Value | 492 kJ |
| Bromelain Complex | 15.0 mg |
| Carbohydrate | 1.7 g |
| Fats | 2.6 g |
| Salt | 1.1 g |
| Protein | 21.0 g |
| Saturated Fat | 0.5 g |
| Sugars | 0.2 g |
| AMINO ACIDS PER 100 G PROTEIN ESSENTIAL | |
| L-Isoleucine (BCAA) | 4.49 g |
| L-Leucine (BCAA) | 8.34 g |
| L-Lysine | 6.85 g |
| L-Methionine | 1.25 g |
| L-Phenylalanine | 5.48 g |
| L-Threonine | 3.89 g |
| L-Tryptophan | 1.06 g |
| L-Valine (BCAA) | 5.11 g |
| CONDITIONALLY ESSENTIAL | |
| L-Arginine | 8.95 g |
| L-Cysteine | 1.10 g |
| L-Glutamic Acid | 17.32 g |
| L-Histidine | 2.51 g |
| L-Proline | 4.56 g |
| L-Tyrosine | 3.83 g |
| NON ESSENTIAL | |
| L-Alanine | 4.43 g |
| L-Aspartic Acid | 11.30 g |
| L-Glycine | 4.24 g |
| L-Serine | 5.31 g |
References
1. Layman, D. K. (2009). Dietary Guidelines should reflect new understandings about adult protein needs. Nutrition & Metabolism, 6(1), 1.
2. Wagenmakers, A. J. (1997). Muscle amino acid metabolism at rest and during exercise: role in human physiology and metabolism. Exercise and sport sciences reviews, 26, 287-314.
3. Joy, J.M., Lowery, R.P., Wilson, J.M., Purpura, M., De Souza, E.O., Wilson, S.M., Kalman, D.S., Dudeck, J.E. and Jäger, R. (2013) ‘The Effects of 8 Weeks of Whey or Rice Protein Supplementation on Body Composition and Exercise Performance’, Nutrition Journal, 12(1), 86.
4. Barbana, C., & Boye, J. I. (2010). Angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory activity of chickpea and pea protein hydrolysates. Food Research International, 43(6), 1642-1649.
5. Krajcovicova-Kudlackova, M., Babinska, K., & Valachovicova, M. (2005). Health benefits and risks of plant proteins. Bratislavske lekarske listy, 106(6/7), 231.
6. Rigamonti, E., Parolini, C., Marchesi, M., Diani, E., Brambilla, S., Sirtori, C. R., & Chiesa, G. (2010). Hypolipidemic effect of dietary pea proteins: Impact on genes regulating hepatic lipid metabolism. Molecular nutrition & food research, 54(S1), S24-S30.
7. Ndiaye, F., Vuong, T., Duarte, J., Aluko, R. E., & Matar, C. (2012). Anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory and immunomodulating properties of an enzymatic protein hydrolysate from yellow field pea seeds. European journal of nutrition,51(1), 29-37.
– Τα συμπληρώματα διατροφής δεν πρέπει να χρησιμοποιούνται ως υποκατάστατο μίας ισορροπημένης δίαιτας.
– Να μη γίνεται υπέρβαση της συνιστώμενης ημερήσιας δόσης.
– Το προϊόν αυτό δεν προορίζεται για την πρόληψη, αγωγή ή θεραπεία ανθρώπινης νόσου. Συμβουλευτείτε τον γιατρό σας αν είστε έγκυος, θηλάζετε, βρίσκεστε υπό φαρμακευτική αγωγή ή αντιμετωπίζετε προβλήματα υγείας.
– Να φυλάσσεται μακριά από τα μικρά παιδιά.
- Food supplements should not be used as a substitute for a balanced diet.
- Do not exceed the recommended daily allowance.
- This product is not intended for the prevention, treatment or cure of a human disease. Consult your doctor if you are pregnant, breast-feeding, under medication or have a health problem.
- Keep out of the reach of small children.
– Να μη γίνεται υπέρβαση της συνιστώμενης ημερήσιας δόσης.
– Το προϊόν αυτό δεν προορίζεται για την πρόληψη, αγωγή ή θεραπεία ανθρώπινης νόσου. Συμβουλευτείτε τον γιατρό σας αν είστε έγκυος, θηλάζετε, βρίσκεστε υπό φαρμακευτική αγωγή ή αντιμετωπίζετε προβλήματα υγείας.
– Να φυλάσσεται μακριά από τα μικρά παιδιά.
- Food supplements should not be used as a substitute for a balanced diet.
- Do not exceed the recommended daily allowance.
- This product is not intended for the prevention, treatment or cure of a human disease. Consult your doctor if you are pregnant, breast-feeding, under medication or have a health problem.
- Keep out of the reach of small children.



 Ελληνικα
Ελληνικα